Menu Board - Tokay Berat Korkut
Introduction
Project Definition
The goal of creating this project is building a web platform that gives many restaurants' food menus. With this webpage people can reach the information of food which are like calorie, price , etc. . My website gives an advantage that people doesn't need to jump from a website to another to seek what they want. They just enter this website and see many restaurants' menus which include many different and timely scheduled food types. As you know every restaurant has at least 2 menus for breakfast and dinner and also they have entries, drinks, desserts etc. When people go to a website that belongs a restaurant , they have to open at least 3 pages that are for main order, drinks and order type to order. This webpage makes things easier for them. They just click on the menu icon and can reach all info in a page.
Starting Point
After coming from Turkey to USA I realized a problem. People can't get correct information about restaurants like what kind of food they have, what the opening and closing times are or what the delivery rules are. So I thought that I can give a option to people to make people reach this information correctly and fast and also people don't want to spend many time to order a food. Because every company has its own website this causes jumping between them to decide what you want to eat. As you notice that these are so much time and effort just to eat a meal. Therefore, I decided to make a platform to collect many fast food companies menus together and also for the restaurants I want to create a platform that people make reservations to go and eat. Other problem about this topic that people have to sign up for every companies websites to order delivery food. This is exactly time spending for nothing. I design my website out of this problem. People will create an account just for one time then, they can order and make reservations whatever and wherever they want.
Technological Details
Platforms
- SquareSpace
Languages
- HTML, HTML5
- CSS
- JavaScript
Definitions of Platforms and Languages
Squarespace[1]: is a SaaS-based content management system (CMS) which is composed of a website builder, blogging platform and hosting service. The service allows individuals and businesses to create and maintain websites and blogs.
HyperText Markup Language[2], commonly referred to as HTML, is the standard markup language used to create web pages. Along with CSS, and JavaScript, HTML is a cornerstone technology, used by most websites to create visually engaging web pages, user interfaces for web applications, and user interfaces for many mobile applications. Web browsers can read HTML files and render them into visible or audible web pages. HTML describes the structure of a website semantically along with cues for presentation, making it a markup language, rather than a programming language. HTML elements form the building blocks of all websites. HTML allows images and objects to be embedded and can be used to create interactive forms. It provides a means to create structured documents by denoting structural semantics for text such as headings, paragraphs, lists, links, quotes and other items. The language is written in the form of HTML elements consisting of tags enclosed in angle brackets (like <html>). Browsers do not display the HTML tags and scripts, but use them to interpret the content of the page. HTML can embed scripts written in languages such as JavaScript which affect the behavior of HTML web pages. Web browsers can also refer to Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) to define the look and layout of text and other material. The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), maintainer of both the HTML and the CSS standards, has encouraged the use of CSS over explicit presentational HTML since 1997.
HTML5[3] is a markup language used for structuring and presenting content on the World Wide Web. It was finalized, and published, on 28 October 2014 by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). This is the fifth revision of the HTML standard since the inception of the World Wide Web. The previous version, HTML 4, was standardized in 1997. Its core aims are to improve the language with support for the latest multimedia while keeping it easily readable by humans and consistently understood by computers and devices (web browsers, parsers, etc.). HTML5 is intended to subsume not only HTML 4, but also XHTML 1 and DOM Level 2 HTML. In particular, HTML5 adds many new syntactic features. These include the new <video>, <audio> and <canvas> elements, as well as the integration of scalable vector graphics (SVG) content (replacing generic <object> tags) and MathML for mathematical formulas. These features are designed to make it easy to include and handle multimedia and graphical content on the web without having to resort to proprietary plugins and APIs. Other new page structure elements, such as <main>, <section>, <article>, <header>, <footer>, <aside>, <nav> and <figure>, are designed to enrich the semantic content of documents. New attributes have been introduced, some elements and attributes have been removed and some elements, such as <a>, and <menu> have been changed, redefined or standardized. The APIs and Document Object Model (DOM) are no longer afterthoughts, but are fundamental parts of the HTML5 specification. HTML5 also defines in some detail the required processing for invalid documents so that syntax errors will be treated uniformly by all conforming browsers and other user agents.
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS)[4] is a style sheet language used for describing the presentation of a document written in a markup language. Although most often used to set the visual style of web pages and user interfaces written in HTML and XHTML, the language can be applied to any XML document, including plain XML, SVG and XUL, and is applicable to rendering in speech, or on other media. Along with HTML and JavaScript, CSS is a cornerstone technology used by most websites to create visually engaging webpages, user interfaces for web applications, and user interfaces for many mobile applications.
JavaScript [5] is a high-level, dynamic, untyped, and interpreted programming language. It has been standardized in the ECMAScript language specification. Alongside HTML and CSS, it is one of the three essential technologies of World Wide Web content production; the majority of websites employ it and it is supported by all modern Web browsers without plug-ins. JavaScript is prototype-based with first-class functions, making it a multi-paradigm language, supporting object-oriented, imperative, and functional programming styles. It has an API for working with text, arrays, dates and regular expressions, but does not include any I/O, such as networking, storage, or graphics facilities, relying for these upon the host environment in which it is embedded. Despite some naming, syntactic, and standard library similarities, JavaScript and Java are otherwise unrelated and have very different semantics. The syntax of JavaScript is actually derived from C, while the semantics and design are influenced by the Self and Scheme programming languages.
CoverPage
HomePage
Menus'Page
Reservations
in Process for this semester
OrderPage
in Process for this semester
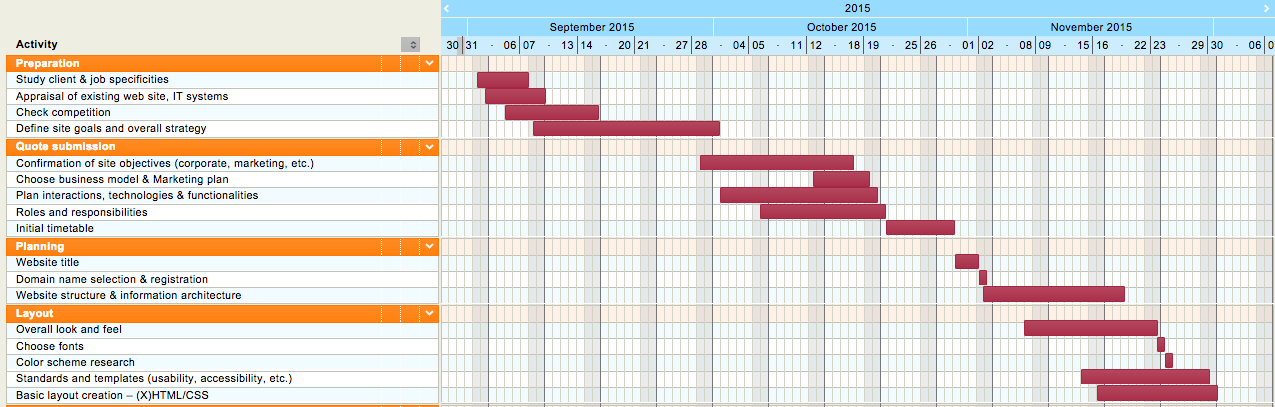
ProjectSchedule
Gantt Charts
Fall Semester
Spring Semester
Expectations from the Project in Spring Semester
Overview and Final View of Project
Overview
Final View of Project
References
1."About Squarespace" from wikipedia : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Squarespace
2."About HTML" from wikipedia : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HTML
3."About HTML5" from wikipedia : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HTML5
4."About CSS" from wikipedia : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cascading_Style_Sheets
5."About JavaScript" from wikipedia : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/JavaScript