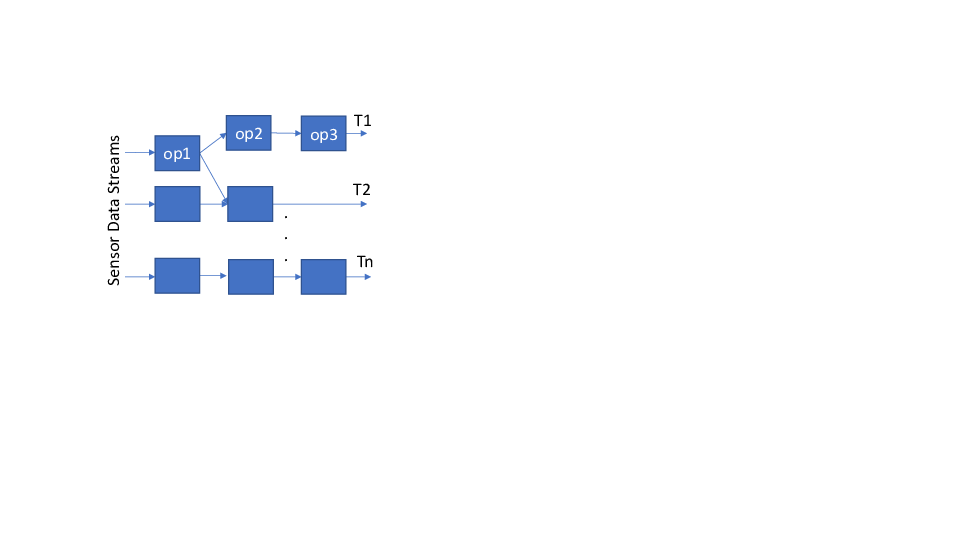
 Timely analysis of real-time sensor data streams is essential to key
applications in the Internet of Things (IoT), such as smart health,
transportation, and energy. Although advanced stream processing engines
(SPEs), such as Apache Storm, Flink, and Spark Streaming, provide
powerful stream processing frameworks in a cloud, sending sensor data to
the SPE for analysis over the wide area network may incur many deadline
misses and create bottlenecks in the core Internet. A viable alternative
is real-time sensor data stream processing in edge devices; however, it
is challenging to support timing constraints using limited resources
available in such devices. Real-time scheduling theory is not directly
applicable, since it is agnostic to data semantics and usually based on
worst-case assumptions for the predictability that would be too pessimistic
and resource inefficient in edge devices. The problem is becoming
increasingly serious as the number of IoT devices and data volume
increases rapidly. The proposed work aims to bridge the widening gap by
investigating cost-efficient approaches for soft real-time stream
processing at the edge. This project explores novel approaches to
scheduling, sensor stream processing, and load sharing to significantly
decrease deadline misses and communicational as well as computational
resource consumption, while enhancing the reliability of real-time
stream processing.
Timely analysis of real-time sensor data streams is essential to key
applications in the Internet of Things (IoT), such as smart health,
transportation, and energy. Although advanced stream processing engines
(SPEs), such as Apache Storm, Flink, and Spark Streaming, provide
powerful stream processing frameworks in a cloud, sending sensor data to
the SPE for analysis over the wide area network may incur many deadline
misses and create bottlenecks in the core Internet. A viable alternative
is real-time sensor data stream processing in edge devices; however, it
is challenging to support timing constraints using limited resources
available in such devices. Real-time scheduling theory is not directly
applicable, since it is agnostic to data semantics and usually based on
worst-case assumptions for the predictability that would be too pessimistic
and resource inefficient in edge devices. The problem is becoming
increasingly serious as the number of IoT devices and data volume
increases rapidly. The proposed work aims to bridge the widening gap by
investigating cost-efficient approaches for soft real-time stream
processing at the edge. This project explores novel approaches to
scheduling, sensor stream processing, and load sharing to significantly
decrease deadline misses and communicational as well as computational
resource consumption, while enhancing the reliability of real-time
stream processing.The research is expected to provide an enabling technology for important IoT applications with great societal impacts, such as those in healthcare, transportation, and energy that produce immense real-time sensor data streams, by substantially improving the timeliness and reliability of real-time stream processing with less resource consumptions compared to state-of-the-art SPEs. The investigator will use select research results to continue education and outreach efforts that include broadly disseminating publications and code that will be produced by this project, developing new courses and teaching materials on real-time stream processing, recruiting underrepresented groups of students to work on the project, and encouraging the younger generation to study computer science and pursue careers in industry and academia.
 This work is supported, in part, by National Science Foundation with Award
Number CNS-2007854
(Award Abstract)
This work is supported, in part, by National Science Foundation with Award
Number CNS-2007854
(Award Abstract)